
The cell is accumulating the building blocks of chromosomal DNA and the associated proteins, as well as accumulating enough energy reserves to complete the task of replicating each chromosome in the nucleus. However, during the G 1 stage, the cell is quite active at the biochemical level.

The first stage of interphase is called the G 1 phase, or first gap, because little change is visible. The three stages of interphase are called G 1, S, and G 2. For a cell to move from interphase to the mitotic phase, many internal and external conditions must be met. * Interphaseĭuring interphase, the cell undergoes normal processes while also preparing for cell division. Usually the cell will divide after mitosis in a process called cytokinesis in which the cytoplasm is divided and two daughter cells are formed. Mitosis is nuclear division during which duplicated chromosomes are segregated and distributed into daughter nuclei. During interphase, G1 involves cell growth and protein synthesis, the S phase involves DNA replication and the replication of the centrosome, and G2 involves further growth and protein synthesis. A cell moves through a series of phases in an orderly manner.

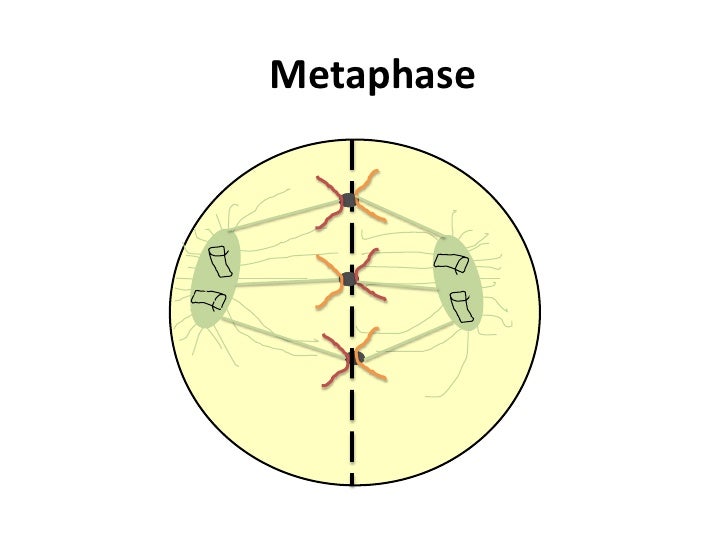
Watch this video about the cell cycle: įigure 1. During the mitotic phase, the replicated DNA and cytoplasmic contents are separated and the cell divides. During interphase, the cell grows and DNA is replicated. The cell cycle has two major phases: interphase and the mitotic phase ( Figure 1). Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, DNA replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. The cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Explain how the three internal control checkpoints occur at the end of G 1, at the G 2–M transition, and during metaphase.
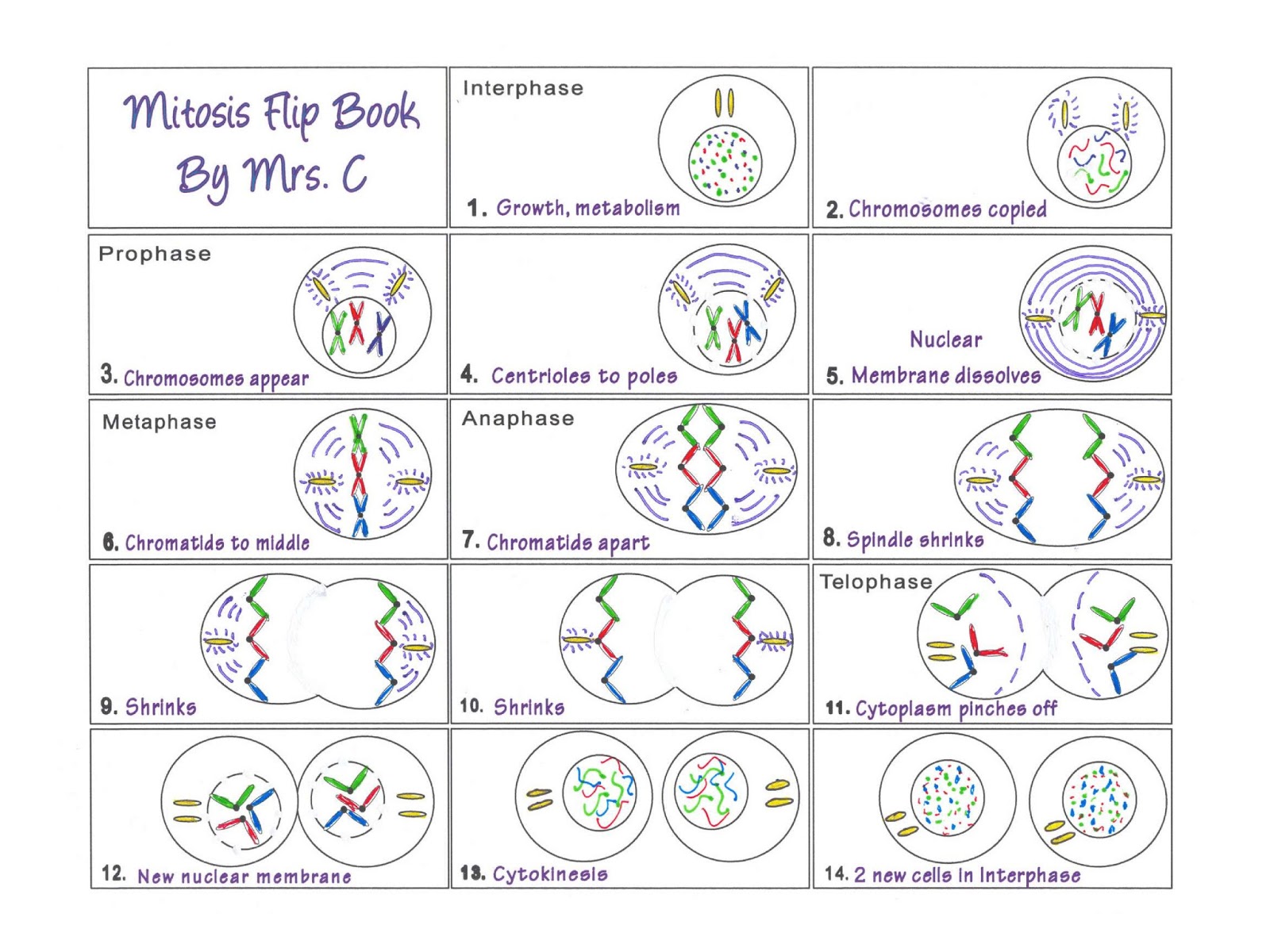
How do the daughter cells compare to the original cell? How does the cell ensure that each daughter cell gets a complete set of genetic information? (IMPORTANT: You do NOT need to memorize the steps of mitosis!) In general terms, discuss what happens during M phase.Describe how the cell cycle functions normally, including what happens during each of the three stages of interphase (G 1, S, G 2) as well as M.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
